Wildlife
Conservation sciences have witnessed an overhaul in the past few decades. With the ever-shrinking buffer between human settlements and wildlife, exclusionary and protectionist forms of conservation are far from effective in addressing the problem at hand. Accounting for human development in conservation practices, and promoting co-dependence has proven to be a much more effective way forward.
Understanding human-animal conflict
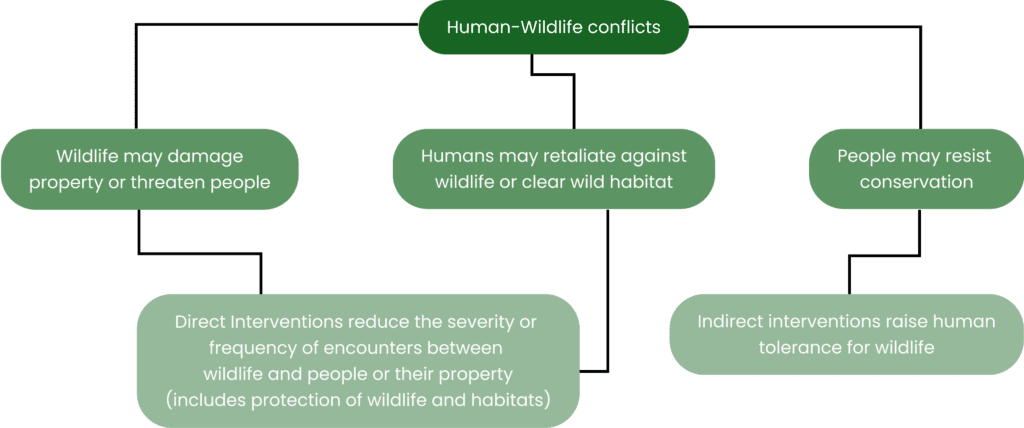
The solution to conflict is fa from simple, and requires a lot of ground-work to understand the extent of human interest, as well as the dynamics of wildlife behavior. There is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to conflict. Conflict mitigation projects should follow a holistic approach by considering a thematic triangle’ of driver-prevention-damage mitigation at various levels.
The ideal output areas are:
- Development of a strategy and action plan to reduce human-wildlife conflict at a national level and in selected states.
- Pilot application of a holistic approach and instruments to mitigate human-wildlife conflicts at pilot sites in three project partner states
- Facilitation of capacity development for key stakeholders to mitigate human-wildlife conflict in India
Steps taken by the government of India to protect Wildlife
- The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 provides for stringent punishment for violation of its provisions. The Act also provides for forfeiture of any equipment, vehicle or weapon that is used for committing wildlife offense(s). Rare and endangered species found in India, have been listed in Schedule-I of the WPA, thereby providing them highest degree of protection.
- Protected Areas, viz., National Parks, Sanctuaries, Conservation Reserves and Community Reserves have been created in the country covering important habitats to provide better protection to wildlife, including threatened species and their habitat.
- Financial assistance is provided to the State/Union Territory Governments under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme of ‘Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats’, for better protection to wildlife and improvement of habitat.
- The local communities are involved in conservation measures through eco-development activities which help the forest departments in protection of wildlife.
- The Wild Life Crime Control Bureau (WCCB) coordinates with State/UTs and other enforcement agencies to gather intelligence about poaching and unlawful trade in wild animals and animal articles.
- Alerts and advisories were issued by WCCB on poaching and illegal trade of wildlife to the concerned State and Central agencies for preventive action.